L-carnosine horsepower

Pro-bodybuilders and top bodybuilders are shy to share knowledge on the chemicals they use to build their physique. The same is even more relevant for the coaches/trainers/nutritionists. They make a living of it. People like Chad Nichols, Charles Glass etc are always looking to find new compounds to improve “their” athletes. Just look at the fact that it took several years before the general bodybuilding adept understood that the physiques they saw in the Weider magazines, used anabolic steroids. Every young bodybuilder followed the training and nutrition programs in those magazines and bought tons of worthless supplements, before they understood that Arnold and friends used Deca, D-bol, Primo and Stano. It’s always kept a secret, just like the newer products, just remember the GH and the insulin protocols. In this light some of the more shady protocols are to be seen like Markus’ interleukines.
In 2005 the renowned strength and conditioning expert Charles Poliquin gave an interview to our “Body of Science” magazine, I posted the whole interview beneath. Charles had many of his Olympic athletes using this procedure during their weight training sessions, and reports excellent success with it. The results he describes are very much in line with what one might expect from reading the research; the muscles have notably greater endurance. According to Charles Poliquin, this is providing tangible benefits in terms of actual tissue gain (size and strength). He believes the buffering is allowing for greater total tonnage in the gym, which allows for more stimulation and more growth.
At the time of this interview (2005) it was very difficult to give practical advice on using injectable Carnosine, as one was practically unable to find pharmaceutical preparation in production. One doesn't want to simply try and home-brew a solution either, as Carnosine is not particularly stable in solution (nor would it be very pure). Any such preparation really needs to be prepared professionally, with proper attention to temperature, pH, sterility, and general product stability. Those using injectable Carnosine a decade ago, where most likely getting a product that originated from a private drug compounding firm, made at the direction of a physician. This was also a very new practice, however, and few people have "caught on" to the use of Carnosine injections as of yet. As word spreads of Olympic and professional athletes using a new "designer agent" this will undoubtedly change very quickly. Until then, a visit to a strength couch like Charles Poliquin may be your only tangible option for experimenting with this.
Veterinary steroids and supplements
Most bodybuilders today have no clue that only a few decades back bodybuilders used veterinary compounds.
They used low dosed veterinary Equipoise (Boldenone), Winstrol that was so thick that one had to use a very thick needle that had to be lubricated first too, what a difference with todays micronized winny.
And bodybuilders known with the potential of Trenbolone Acetate extracted their Tren from veterinary pellets with acetone, speaking of purity!! What I want to make clear to you is that farmers have a much more interest in lean musclemass packed on their cattle and poultry, because they sell their animals for meat consumption and improved mass makes an improved slaughter weight and thus money. That’s why in those years many people imported veterinary gear from Australia and when Aussie business flourished, Australian companies opened a Mexican branch company to supply the enormous US market. Most young bodybuilders forgot about the mixed pharmaceuticals like Drive, Spectriol, Geldabol and Filibol Forte, often spiked with Methandriol Dipropionate.
Veterinary compounds generate so much money it literary dwarfs the price money made by bodybuilding contests. The same is of course true with athletes ( just look at Fuentes and Ferrari). And today in the horse- greyhound- and camel races so much money is involved, not only pricemoney, but also the profits with betting. That’s why organistions in by example Dubai are preparing and doping animals that normally have no change to win. That’s why today very much knowledge enters our sport and compounds like injectable Carnosine and Kynoselen (used as a recovery compound after a race and some time ago used in bodybuilding) are easy to purchase. That’s why I write this blogpost for you guys.
Carnosine is a histidine-containing dipeptide, comprised of a chemical combination of the amino acids beta-alanine and L-histidine. The exact role of Carnosine in the human body is not fully understood, but it is believed to play a role as antioxidant, neurotransmitter, and protective nutrient against cell aging. Carnosine is currently on its way to becoming a popular general health supplement, due to its perceived role in preserving good health and slowing the cellular damage of aging. Dietary supplements containing Carnosine, however are not the subject of this profile. We are discussing injectable Carnosine here, or more specifically the practice of using intramuscular injections of Carnosine to improve athletic performance. In this regard it is being used to reduce muscle fatigue, increase muscle endurance, and extend the overall capacity for work.
The interest in using Carnosine to enhance athletic performance becomes fairly obvious when we look at the role this nutrient plays in human muscle physiology. Carnosine has been shown to contribute to physiochemical buffering in exercised muscles. You may be familiar with the practice of Sodium Bicarbonate (baking soda) loading, which loosely works on the same principle. Carnosine acts as a buffering agent because of its L-histidine content. As the muscles are taxed during exercise, and lactic acid begins to build, Carnosine beings to break down at a high rate. Free amino acids are formed, as the chemical bonds holding them together are broken. The histidine this process yields helps to maintain acid-base (pH) balance in the muscles, allowing them to work at a higher capacity for a longer period of time. Studies have shown that Carnosine concentrations correlate closely with the maximum power output capacity of the muscles.
The typical practice for using Carnosine involves injecting l-2 grams of the nutrient into the bellies of the muscles that are to be trained that day. Small muscle groups such as the deltoids and biceps may take a single injection in each side, while larger muscle groups may require placing smaller injections into more than one area of tissue to better distribute the nutrient. The injections are administered within 3 minutes before training, so that local levels of Carnosine are at their highest.
Carnosine 10 years ago
L-carnosine (AKA carnosine), a naturally occurring combination of two amino acids, was discovered in Russia in the early 1900s. Because much of the pioneering research was done in Russia, it was largely unavailable to the rest of the world until a number of studies and experiments in other parts of the world began verifying those studies -- and more.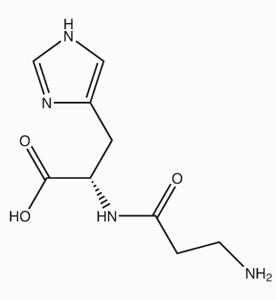
Most notably, there were a series of astonishing experiments done in Australia that proved that carnosine rejuvenates cells as they approach senescence (the stage just before death where a cell is still alive, but essentially non-functional). The studies showed that cells cultured with carnosine lived longer and retained their youthful appearance and growth patterns.
What's probably the most exciting result of the studies is that it was discovered that carnosine can actually reverse the signs of aging in senescent cells.
How to Reverse Aging in Cells
In one study, when scientists transferred senescent cells to a culture medium containing carnosine, those cells exhibited a rejuvenated appearance and often an enhanced capacity to divide. When they transferred the cells back to a medium lacking carnosine, the signs of senescence quickly reappeared.
As they switched the cells back and forth several times between the culture media, they consistently observed that the carnosine medium restored the juvenile cell phenotype within days, whereas the standard culture medium brought back the senescent cell phenotype. In addition, the carnosine medium increased cell life span -- even for old cells. When the researchers took old cells that had already gone through 55 divisions and transferred them to the carnosine medium, they survived up to 70 divisions, compared to only 57 to 61 divisions for the cells that were not transferred.
This represents an increase in the number of cell divisions for each cell of almost 25%.
But in terms of cell life, the increase was an astounding 300%. The cells transferred to the carnosine medium attained a life span of 413 days, compared to just 126 to 139 days for the control cells.
Increase Life Expectancy
A Russian study on mice subsequently showed that mice given carnosine are twice as likely to reach their maximum lifespan as untreated mice. Carnosine also significantly reduces the outward "signs of old age."
In effect, it makes the mice look younger. 44% of the carnosine treated mice had young, glossy coats in old age as opposed to only 5% in the untreated mice. This represents 900% better odds of looking young in old age.
Another important difference between the treated and the untreated mice was in their behavior. Only 9% of the untreated mice behaved youthfully in old age, versus 58% of the carnosine treated mice. That's a 600% improvement in how they felt.
According to a recent study done at the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, carnosine [ also delays the ageing process. And if you take beta-alanine, you increase the amount of carnosine in your muscle cells. 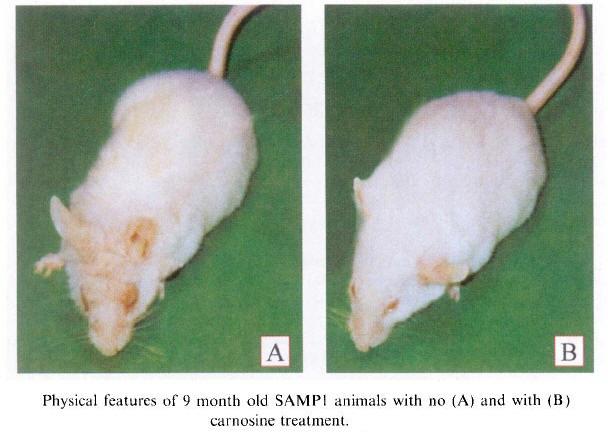
The researchers have been studying the life-extending properties of carnosine since the nineties. In 1999 they announced that carnosine supplements extended the lifespan of fast-ageing mice and in 2002 they published the results of a study in which fruit flies that had been given carnosine in their food lived longer
Fruit flies were also used in the study referred to here. Male and female fruit flies were given food that had carnosine mixed in with it, plus two tweaked versions: molecules consisting of a carnosine part and a vitamin E part. The researchers used S,S-trolox-carnosine [STC] [structural formula shown above] and R,S-trolox-carnosine [RTC].
Carnosine extended the lifespan of the male fruit flies by 20 percent, but had no effect on the life expectancy of the female fruit flies. STC extended the lifespan of both the females [by 36 percent] and the males [by 16 percent]. RTC had no effect.
Protein Glycation: Sugar and Aging
Glycation is the uncontrolled reaction of sugars with proteins. It's kind of like what happens to sugars when you heat them and they caramelize. In effect, glycation is what happens when excess sugars and/or alcohols caramelize the proteins in your body. It's a major factor in the aging process -- and it's particularly devastating to diabetics.
Your body is mostly made up of proteins. In fact, proteins are the substances most responsible for the daily functioning of your body. That's why anything that causes protein deterioration has such a dramatic impact on the body's function and appearance.
Thanks largely to the destructive effect of sugar and aldehydes (compounds formed by the oxidation of alcohol), the protein in our bodies tends to undergo destructive changes as we age. This destruction is a prime factor, not only in the aging process itself, but also in the familiar signs of aging such as wrinkling skin, cataracts, and the destruction of our nervous system -- particularly our brains. Studies show that carnosine is effective against all these forms of protein modification.
Protein Modification for Longevity
As I said, aging is associated with damage to cellular proteins. But carnosine protects cellular proteins from damage in at least two ways.
Carnosine bonds with the carbonyl (or aldehyde) groups that if left alone will attack and bind with proteins.
It works as an antioxidant to prevent the formation of oxidized sugars, also called Advanced Glycosylation End-products or AGEs for short. That's really the caramelization thing that I mentioned earlier. The bottom line here is that the less AGEs, in your body, the younger you are.
Both of these processes have important implications for anti-aging therapy. The key is that carnosine not only prevents damaging cross-links from forming, it eliminates cross-links that have previously formed in proteins, thus restoring normal membrane function in cells.
Preventing Alzheimer's
Carnosine has been proven to reduce or completely prevent cell damage caused by beta-amyloid (AKA amyloid-beta, amyloid ß-protein, and Aß), one of the prime suspected protein risk factors for Alzheimer's. The presence of beta-amyloid leads to damage of the nerves and arteries of the brain. Carnosine blocks and inactivates beta-amyloid. In effect, it protects neural tissues against dementia. The key is that carnosine not only prevents damaging cross-links from forming in proteins, it eliminates cross-links that have previously formed in those proteins, thus restoring normal membrane function in cells. This is true not only in the brain, but in all the organs of our body -- our skin included. Keep in mind that the damage you see in the skin is not just a cosmetic question. That damage is absolutely an indicator of the kinds of damage happening to every other organ in your body -- including your eyes and your brain.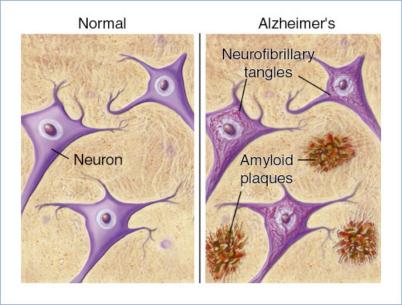
It should be noted that although still "unproven," the beta-amyloid connection to Alzheimer's is nevertheless the dominant theory as to its primary cause. The mainstay of the amyloid ß-protein hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease is that a gradual and chronic imbalance in the production versus the clearance of Aß leads to a slow rise in its steady state levels in brain tissue. This leads to beta-amyloid plaque accumulation and subsequently, to the complex molecular and cellular changes associated with the disease. Thus anything that helps inhibit excess beta-amyloid accumulation in the brain -- or even better, helps remove it -- is likely to be Alzheimer's protective.
Auto-Regulator
Carnosine has the remarkable ability to throttle down bodily processes that are in a state of excess, and to ramp up those that are under expressed. For example, carnosine thins the blood of people whose blood tends to clot too much and increases the clotting tendency in those with a low clotting index.
Another example is that carnosine suppresses excess immune responses in those who have "hyper" immune systems, whereas it stimulates the immune response in those with weakened immune systems -- such as the aged. This is a critical benefit for people with allergies and people with autoimmune disorders.
And, as a neurotransmitter, carnosine even seems to have the ability to normalize brain wave functions. In fact, studies indicate that carnosine might play an invaluable role in helping to prevent and control seizures.
Carnosine -- the New Studies
And that's where things stood when I first wrote about carnosine ten years ago. Since then, the evidence of carnosine's benefits has continued to pour in. For example, a 2010 study published in Rejuvenation Research found that adding carnosine to the diet of fruit flies produced a 20% increase in the average life span of male flies. Curiously, it had no effect on the lifespan of female flies -- until water-soluble vitamin E was also added. At that point, female flies experienced an immediate 36% increase in longevity. Although fruit flies are not human beings, this study confirms observations already seen in human subjects. Note: the reason for using fruit flies as test subjects is that their short lifespan allows for quick observation on whether a nutrient increases lifespan or not. By itself, this study may not mean a lot, but when analyzed in the context of the following studies, it's extremely powerful.
Carnosine helps control blood glucose
A recent study found that there is evidence that the release of carnosine from skeletal muscle during physical exercise affects autonomic neurotransmission and physiological functions. In particular, carnosine positively impacts the activity of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves that supply energy to the adrenal glands, liver, kidney, pancreas, stomach, and white and brown fat tissues, thereby causing beneficial changes in blood pressure, blood glucose, appetite, lipolysis, and the thermogenic burning of fat. In summary, carnosine lowers elevated blood sugar levels, improves insulin production and sensitivity, and promotes the loss of weight and body fat. And if this were not enough, studies have shown that people who are diabetic or even pre-diabetic have lower-than-normal carnosine levels in both their muscle and brain cells -- levels about 63% below normal, which is similar to levels found in people in their 70's. 
The bottom line is that in addition to its life extension benefits, L-carnosine is beginning to emerge as an indispensible supplement for diabetics. It not only helps control primary factors in the onset of diabetes, but it also protects against diabetic echo effects such as organ protein degradation, loss of kidney function, damage to the eyes, neuropathy, and cardiovascular damage -- not to mention actually helping the heart muscle contract more efficiently.
Carnosine Helps with Wound healing
In a study published just last month, treatment with L-carnosine enhanced wound healing significantly. In addition, wound tissue analysis showed increased expression of growth factors and cytokines genes involved in wound healing. And even further, in vitro analysis of human dermal fibroblasts (the cells that promote skin healing) and microvascular-endothelial cells (the cells responsible for regenerating new blood vessels after injury) showed that carnosine increases cell viability in the presence of high glucose. But this is not only important for diabetics. In fact, wound care for the elderly in long term and acute care facilities is often extremely difficult -- not to mention very costly for the facilities involved. Again, the connection between seniors in general and people with diabetes is the dramatically lower levels of carnosine in their cells shared by both groups. In other words, the benefits in wound healing experienced by diabetic patients is likely to be seen by the general senior population as well.
Animal study: carnosine slows down tumour growth
Carnosine, the dipeptide that the body synthesises from beta alanine, not only helps muscles cells work harder. Researchers at the University of Leipzig discovered that carnosine also inhibits the growth of cancer cells.
In 2008 the Germans published the results of a study in which cells from a human glioblastoma – a form of brain tumour that is almost impossible to treat – grew less fast when they were exposed to carnosine.
This miniscule protein sabotages the cancer cells' energy provision, and reduces the conversion of carbohydrates into the energy molecule ATP. Glucose is cancer cells' preferred source of fuel.
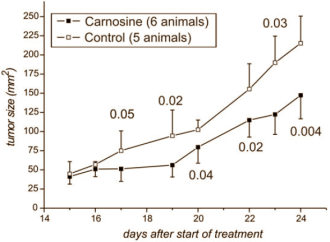
Of course, a substance that reduces cancer cell activity in a test tube might not actually work in real life. To approximate a human flesh and blood scenario the researchers did an experiment with mice. The Germans injected the mice with cancer cells that cause increased synthesis of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 [HER2/neu], a protein.
Tumours need blood to grow. Many extra dangerous cancer cells secrete raised concentrations of HER2/neu. This protein forces the body to create new blood vessels so that the tumour is provided with extra blood.
Half of the mice were given an injection nearly every day of a regular salt solution, directly into their gut. This was the control group. The other half were given a carnosine injection a similar number of times. To be more precise: the mice were given a peritoneal injection containing 500 microlitre fluid with 1 mol carnosine, 6 times a week.
In the control group the tumours started to grow after 14 days; in the carnosine group growth didn't start until the 19th day. On day 24, at the end of the treatment period, the tumours in the carnosine mice were about thirty percent smaller than in the control group.
When the researchers examined the tumour cells under the microscope, they saw that the carnosine had reduced the cell division. In test tubes they also noticed that the cancer cells produced less ATP. 
"Carnosine should be considered as a potential anticancer agent, especially since it is a naturally occurring substance", the researchers write. "It is now very important to analyse how carnosine inhibits proliferation and whether it may be a useful drug for anticancer therapy in humans."
Carnosine Protects Against the Side Effects of Chemotherapy
The protective effects of carnosine in mouse bone marrow cells against damage to their genetic structure caused by the chemotherapy drug cyclophosphamide were reported in the April issue of Cell Biochemistry and Function. In the study, mice were injected with solutions of carnosine at different doses for five consecutive days. On the fifth day of treatment, mice were injected with the highly toxic chemotherapy drug, cyclophosphamide. Blood cells and bone marrow were then examined. Carnosine significantly reduced both damage to blood cells and bone marrow toxicity normally induced by cyclophosphamide. It appears that the antioxidant capabilities of carnosine reduced the oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by the chemotherapy drug.
In addition, cancer researchers are starting to identify how carnosine's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capabilities may not only play a chemoprotective role, but actually help protect against cancer itself. How? First, as just mentioned in the paragraph above, carnosine helps block DNA damage that can lead to transformation of healthy cells into malignant cells. In addition, it has demonstrated a significant ability to both inhibit tumor growthas well as the metastasis of existing cancers.
Carnosine Protects Against Alcohol Induced Liver Damage
In yet another confirmation of carnosine's ability to protect against damages from excess levels of sugar and alcohol in the bloodstream, a study published in the June issue of Toxicology and Industrial Health has shown that supplementation with carnosine is effective for both preventing and repairing biochemical alterations and morphologic damage in the liver caused by exposure to alcohol. In other words, regular supplementation with carnosine might be worth considering if you're prone to regularly party down. I.m.o. the same liver protecting properties could be true guys using oral steroids.
Carnosine Protects Your Brain
Two facts lend more credence to the idea that supplemental carnosine is beneficial to your brain. First, it has been known for some time that brain tissue naturally contains high levels of carnosine, which are capable of reducing the oxidative and glycemic stresses to which the brain is especially vulnerable. Carnosine in brain tissue reduces inflammation, a harmful factor in and of itself, and as we've already discussed, carnosine reduces the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaque in the brain, a probable key factor in the onset of Alzheimer's. And of course, as I discussed 10 years ago, carnosine is an effective heavy metal chelator that crosses the blood-brain barrier and thus can help reduce the toxic impact of heavy metals that may accumulate in the brain. 
The second key fact is that more recent studies have shown that carnosine levels are actually significantly lower in patients with Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease than in people without those problems. This might indicate either a carnosine deficiency that allows for the onset of the diseases (remember that carnosine levels are dramatically lower in pre-diabetics, diabetics, and the elderly) or that the diseases themselves exhaust the carnosine supplies in the brain. Or both together! Either way, numerous studies now point to the role carnosine might play in both protecting the brain from Alzheimer's and even Parkinson's disease, for that matter. Even more exciting, sufficient supplementation with carnosine may even play a role in helping to reverse at least some of that damage.
Conclusion
Make no mistake; L-carnosine may no longer be "new" news. And it may no longer be trendy; but it still ranks as one of the most important anti-aging supplements available to us today. Not only is it protective for all of the long-term conditions mentioned above, but it is probably the single supplement most likely to produce a visible "youthening" of your appearance in the shortest possible time -- three to six months.
The following may not be scientific proof, but it is worth considering. I'm turning 65 in February, and my sister still calls me Peter Pan. In fact, even though she's five years younger than I am, she always introduces me as her younger brother -- to avoid questions. I've been supplementing with 1,500 mg of carnosine a day (using my own formulas) for 10 years now. My skin looks years younger than my age. Neither my sister nor any of my other siblings supplement with carnosine. They don't look the same, so we're not talking genetics here.
It may not be scientific, double-blind-study proof -- but I'm just sayin!


