Age Management
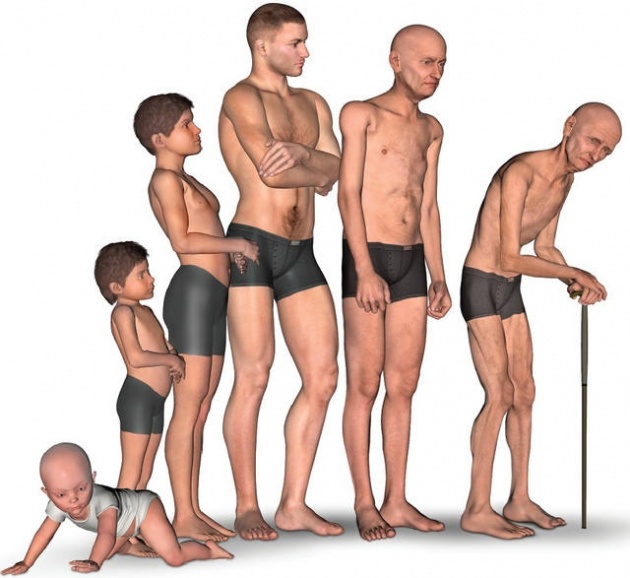 You should assume that science had already developed a sound believable theory about the causes of aging. Unfortunately, a comprehensive explanation is not -yet- available. So far, there are no fewer than 18 different theories that attempt to map the phenomenon of aging from various angles. Where the experts do agree on is the evolutionary usefulness of aging. To put it very crudely: nature is not interested in the individual, but in the species. The survival of the species is the primary, if not sole purpose of evolution, say of nature. In practice, this means that man (and this is actual true for all life forms) for nature is only really important in the period of maximum fertility, the timespan we can reproduce ourselves. In practice, this is the lifespan of optimal sexual maturity, so somewhere between thirteen and thirty years. Nowadays it is normal that women have children after their 45th and men can still father if they are eighty or older. But with the increasing age, the chance of conceiving healthy offspring gets smaller and increases the likelihood of the number of children with congenital derogation. It is primarily because of the improved hygiene the increased medical knowledge, that our life expectancy is longer than 30 to 40 years.
You should assume that science had already developed a sound believable theory about the causes of aging. Unfortunately, a comprehensive explanation is not -yet- available. So far, there are no fewer than 18 different theories that attempt to map the phenomenon of aging from various angles. Where the experts do agree on is the evolutionary usefulness of aging. To put it very crudely: nature is not interested in the individual, but in the species. The survival of the species is the primary, if not sole purpose of evolution, say of nature. In practice, this means that man (and this is actual true for all life forms) for nature is only really important in the period of maximum fertility, the timespan we can reproduce ourselves. In practice, this is the lifespan of optimal sexual maturity, so somewhere between thirteen and thirty years. Nowadays it is normal that women have children after their 45th and men can still father if they are eighty or older. But with the increasing age, the chance of conceiving healthy offspring gets smaller and increases the likelihood of the number of children with congenital derogation. It is primarily because of the improved hygiene the increased medical knowledge, that our life expectancy is longer than 30 to 40 years.
The Neuroendocrine Theory
F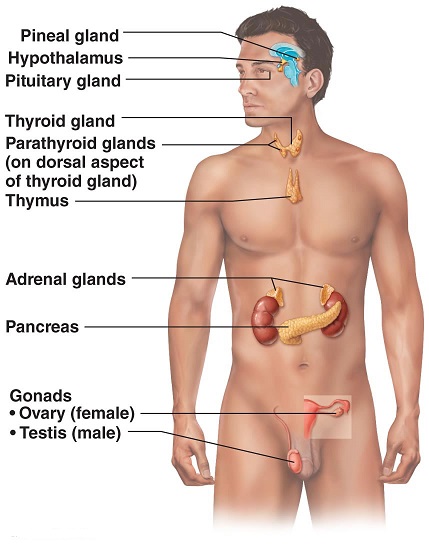 irst proposed by Professor Vladimir Dilman and Ward Dean MD, this theory elaborates on wear and tear by focusing on the neuroendocrine system.
irst proposed by Professor Vladimir Dilman and Ward Dean MD, this theory elaborates on wear and tear by focusing on the neuroendocrine system.
As long as we are young hormones are available in bountiful quantities. Hormones are produced by various glands and tissues and released into the bloodstream. Think of the testes (testosterone), ovaries (estradiol), thyroid (thyroxine) pancreas (insulin and glucagon) and liver and tissues (IGF 1).
This whole process is controlled by the hypothalamus, a gland located deep within the brain with the size of a chestnut, which links the nervous system to the endocrine system. The hypothalamus triggers the pituitary gland to produce trophic hormones, substances which each transmit the necessary signals. Furthermore, the hypothalamus registers and governs, body temperature, blood sugar, appetite and a number of other important physiological and psychological processes.
With advancing years the production of most hormones decreases. Testosterone by example decreases per decade on average 10%. Growth Hormone (hGH) also decreases significantly after the age of thirty, while the pituitary of people over 44 to 50 years responds less, or even no longer, to “hormone releasers”.
As we grow older the hypothalamus loses it precision regulatory ability and the receptors which uptake individual hormones become less sensitive to them. Not only, the secretion of many hormones declines as we age, but their effectiveness (compared unit to unit) is also reduced due to the receptors down-grading.
Low blood levels of (free) testosterone and hGH reduces the effectiveness of mental and physical processes. There is an abundance of literature suggesting that low testosterone is associated with depression and a number of undesirable physical changes such as increased fat deposition (especially in the peritoneum) and breakdown of muscle mass. The storage of fat in the abdominal cavity is one of the most visible signs of degeneration.
T hese are some of the reasons that Dr. Dean recommends receptor resensitizers such as the bi-guanidine drug Metformin (which improves insulin sensitivity) and the eugeroic drug Modafinil (which improves noradrenaline sensitivity).
hese are some of the reasons that Dr. Dean recommends receptor resensitizers such as the bi-guanidine drug Metformin (which improves insulin sensitivity) and the eugeroic drug Modafinil (which improves noradrenaline sensitivity).
One theory for the hypothalamus loss of regulation is that it is damaged by the hormone cortisol. Cortisol is produced from the adrenal glands (located on the kidneys) and cortisol is considered to be a dark-hormone responsible for stress. It is known to be one of the few hormones that increases with age.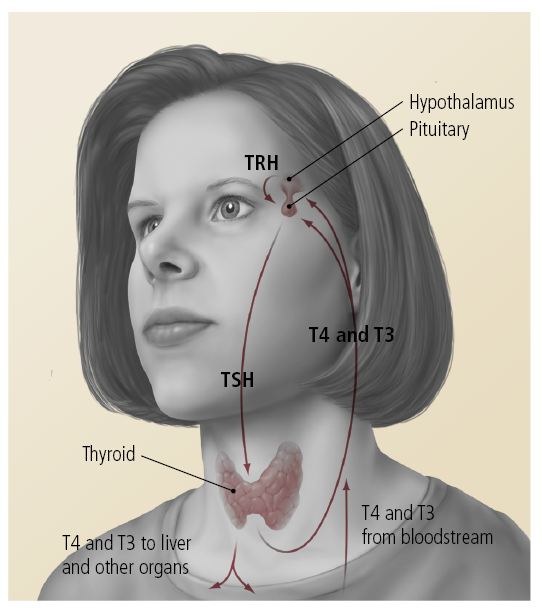
If cortisol damages the hypothalamus, then over time it becomes a vicious cycle of continued hypothalamic damage, leading to an ever increasing degree of cortisol production and thus more hypothalamic damage. A catch-22 situation.
This damage could then lead to hormonal imbalance as the hypothalamus loses its ability to control the system. Such an argument demands the use of cortisol adjusters (such as DHEA or Phenytoin) to help slow down the cortisol accumulation.
Dr. Dean also believes that the next-generation of hormone replacement therapy are the hypothalamus hormones (expected to be commercially available in the next few years). These types of natural supplements could present a whole new approach and concept to endocrine balance, control and improvement.
Hormone Balance and Longevity
Hormones are the biochemical messengers of the neuroendocrine system, a complicated network of chemicals, glands, nerves and feedback loops that orchestrates actions of cells and systems throughout the body. They keep our metabolism and immune systems running in smooth order.
Our bodies function at peak efficiency in our youth when hormones are at their highest. It is at that time that our immune system is generally at its strongest; we build muscle instead of fat, injuries heal quickly, energy is plentiful.
Decline in key hormones is a primary cause of aging. Many respected scientists believe that recreating the fined tuned hormone balance of youth is fundamental in controlling aging.
Individual Assessment is Essential
As we age, the ability to produce and release certain hormones diminishes. An individual’s genetics, nutrition, exercise levels, stress and lifestyle all play an inextricable role in how this occurs. Clearly the aging process itself is different for each individual so any longevity plan must be tailored to meet each person’s needs and goals. This is especially true when the discussion of hormone replacement arises. Careful assessment of laboratory findings and how they relate to each individual experience of hormone change is essential in the decision making process.
Chronological Age vs Biological Age aka Nature or Nurture
According to science, there’s a difference between chronological age and biological age, which means you can be 50 years old and literally have a body of a 40 year old. I’m sure you’ve met someone that not only looks 10 years younger, but has boundless energy and stamina. That being said, I’m sure you’ve seen the exact opposite as well, someone that looks and acts much too OLD for their actual age.
S o what’s the deal? Is it genetics? I know it sounds like the most reasonable answer. But genetics have very little to do with how fast or slow you age. Believe it or not, YOU have way more control over the aging process than you think.
o what’s the deal? Is it genetics? I know it sounds like the most reasonable answer. But genetics have very little to do with how fast or slow you age. Believe it or not, YOU have way more control over the aging process than you think.
The protein collagen is at the heart of this theory. Collagen, akin to the body's glue, is one of the most common proteins making up the skin, bones, ligaments, and tendons. When we're young, collagen is pliable. But with age, collagen becomes more rigid, and it shrinks. That's why your skin is less elastic than before.
Aesthetics aside, cross-linking may block the transport of nutrients into cells as well as obstruct waste-product removal. Free radicals are destructive marauders roving your body, ready to pounce on healthy cells. They are produced as part of the millions of chemical reactions your body performs to sustain life.
Y our body also makes them in response to environmental toxins such as excessive amounts of unprotected sunlight and cigarette smoke. Free radicals oxidize your cells (think rusting metal). As unbalanced, volatile oxygen molecules, they sacrifice healthy cells to make themselves more stable.
our body also makes them in response to environmental toxins such as excessive amounts of unprotected sunlight and cigarette smoke. Free radicals oxidize your cells (think rusting metal). As unbalanced, volatile oxygen molecules, they sacrifice healthy cells to make themselves more stable.
In doing so, free radicals destroy or alter DNA, the cell's genetic blueprint, and disrupt many other cell functions. Free radicals may kill cells as a result of their marauding, or they may give rise to mutant cells that can lead to chronic conditions including cancer and heart disease. Fortunately, the body maintains a sophisticated defense system against free radicals. Unfortunately, our defenses wane with time, and cell damage ensues.
This theory could also be called The Use It and Lose It Theory. The idea is that use, and overuse, of your organs pushes them to the brink of destruction. A poor diet, too much alcohol, and cigarette smoking are thought to accelerate natural wear and tear. With age, the body is less able to repair itself. I think it is obvious that marihuana and hard drugs aren’t helpful either. But like you see on Arnolds picture, use and abuse are two completely different things!! Alcohol on occasion, some pot or junk-food aren’t that bad unless you do it constantly. And for the bodybuilders in conjunction with AAS.
How does wear and tear occur? Free radicals, which inflict cellular damage, may be culpable. Similar to the wear and tear idea, this theory says you are born with a certain amount of energy. If you live "fast," you die young, because you use up your energy reserves sooner. "Laid-back people," who suffer from less stress and take life easier, would live longer should this theory prove correct.
Hormones-Sex and Much More!
Of course, when anyone speaks of h ormones, the first thought in most minds is their reference to sex. And, yes, healthy hormone levels are essential for libido, performance and pleasure. 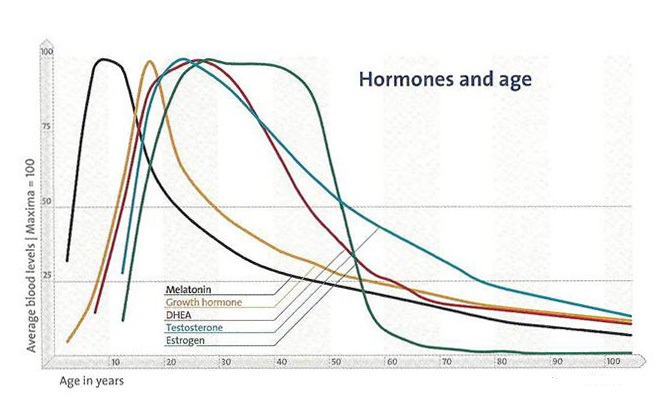 Perhaps, less generally known are hormones’ essential role in the harmonious orchestration of body and brain activity. Their decline to a fraction of what they were in our youth may set the stage for the mind-body deterioration we associate with "old age". Here are some of the hormones which are tested in an anti-aging program:
Perhaps, less generally known are hormones’ essential role in the harmonious orchestration of body and brain activity. Their decline to a fraction of what they were in our youth may set the stage for the mind-body deterioration we associate with "old age". Here are some of the hormones which are tested in an anti-aging program:
DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone)- sometimes referred to as the "mother of all steroids" is the most abundant steroid hormone in the human body. It is the precursor to testosterone and estrogen. DHEA is five to six times more concentrated in the brain where it protects, in particular, from the ravages of excess cortisol. Additionally, it stimulates growth hormone receptors and modulates insulin sensitivity, diabetes, and obesity; it is a potent immune booster and has benefits in memory and cognitive processes, collagen and skin integrity and may help with depression and insomnia.
Pregnenolone- is the foundation hormone for other hormones including DHEA, progesterone, and testosterone. It is produced from cholesterol in the mitochondria (the energy powerhouse of the cell). Studies have shown that it has a potent stimulatory effect on the memory and cognitive function of brain and also helps block the effects of cortisol. Other benefits may include anti-inflammatory properties, improved mood and sleep, enhanced sense of wellbeing.
Testosterone- generally known for promoting sex drive in both men and women, this hormone plays an important role maintaining muscle skin and bone integrity. It strengthens the immune system and increases some mental functions particularly visual spatial ability. Estrogen- generally considered a female hormone; it is produced in small amounts in men. It has a positive effect on many organs throughout the body. It protects against coronary artery disease, improves lipids and raises good (HDL) cholesterol. Estrogen preserves bone density, and supports collagen formation. It has positive effects on mood, memory and concentration and some studies have shown may help stimulate the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, preventing Alzheimer’s.
Progesterone- works together with estrogen in more than 300 receptor sites in the body. It is also a precursor for other hormones. Progesterone has a large number of functions and benefits on its own including promoting fat breakdown, maintaining bone, increasing energy, normalizing blood sugar, improving mood and protecting against cancer. Thyroid- these hormones are vital in the regulation of metabolism and the production of other hormones. Thyroid hormone balance is crucial for health. Excess or inadequate thyroid function has detrimental effects on virtually every system. Obesity, heart disease, infertility, hair loss, mental illness, lethargy, visual disturbances, osteoporosis are just a few conditions arising from thyroid dysfunction.
Melatonin- is a hormone known for its role in controlling our body’s clock. It has been suggested that it may even control the aging clock of the brain. It is a key player in our sleep/wake cycles.
It is used a sleeping aid and also assists in recovery from jet lag. It is now recognized as a key element in maintaining hormonal balance. Additionally, melatonin is a potent anti-oxidant capable of scavenging free radicals working both on the inside and outside of every cell. It also stimulates the thymus gland (the key organ of the immune system) involved in the production of disease-fighting T-cells. Laboratory research has shown that decreasing melatonin accelerates aging and restoring melatonin re-establishes youthful function. Human Growth Hormone (hGH)-is the primary hormone produced by the pituitary gland and regulates all other hormones levels within the body. It has been referred to as the "fountain of youth hormone" due to its remarkable role in deterring the effects of biological aging. HGH affects almost every cell in the body. Like other hormones, it begins to decline with age losing about 14 % per decade after age 30 to levels by the age of 65 that are less than half of what anti-aging researchers consider optimal. In many people, it can be replaced naturally by a program that combines nutrient supplementation, amino acid precursors that effectively stimulate the pituitary to produce hGH, exercise (especially weight training), and a diet that keeps insulin in check. This is the natural approach we choose at our clinic. For those with whom this approach fails to achieve desired results, daily injections of recombinant DNA growth hormone, may be an option they could investigate.
Human growth hormone (HGH or Somatotropin)which can produce increases in the levels of insulin-like growth hormone 1 (IGF-1). There is a direct connection between the level of this hormone in a human’s body, and their age. If this hormone could be kept at the levels of youth, then would the aging process be slowed down, or even stopped altogether? It is a question that has spawned much controversy within the ranks of physicians, with many leading doctors on both sides of the issue. The majority of antagonists, I would venture to guess, have no clinical experience using neither HGH nor the GH releasers (Sermolerin, GHRP2 and GHRP-6). In the beginning of this blogpost I already mentioned the fact that after a certain age GH releasers don’t work anymore.
Effects of Human Growth Hormone Decline:
The decline in human growth hormone is directly tied to the bulging, wrinkling, saggy, flabby, tired creatures that we eventually morph into. Those of us who have naturally lower amounts of hormone age much faster than those of us with good genes. Those who exercise hard also maintain a higher GH level. It’s either that or GH injects.
Documented benefits of hGH therapy - increased lean body mass and muscle strength -decreased body fat, especially in the abdomen- increased bone density- improved skin thickness and diminished wrinkles- better energy and exercise recovery- improved sleep and emotional stability- increased immune response- improved sexual function- better lipid profiles- increased well-being, cognitive function and mental alertness.
A Final Note on Hormones
Different hormones perform different functions in the body, but they all work synergistically. There are reasons why all these hormones are in the body and why our body and mind function at their peak efficiency when these are at optimal levels and balance.
All of us would like to have the best quality of life for as long as we live. And we are living longer. Today, we can explore effective new health care choices that can positively influence longevity and quality of life.
Bodybuilders are often present on the bodybuilding discussionboards, but maybe we should visit other discussionboards such as the Life Extension Forum (LEF) and/or other longevity boards, to broaden our view, especially when we are getting older.



